Verb
Verbs are mostly used words in writing and speech. Any writing or speech without verb is incomplete. Verbs may show an action or a state.
Verb Definition
A verb is a word which expresses action or a state of being or condition. OR A word that describes an action, condition, or experience.
Examples: Go, feel, read, laugh, write, eat, seem
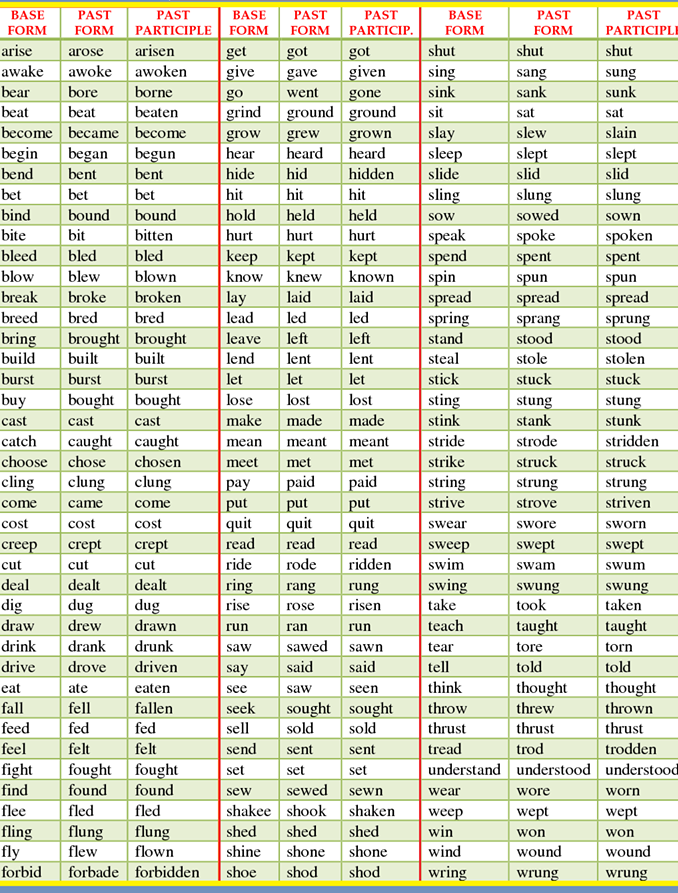
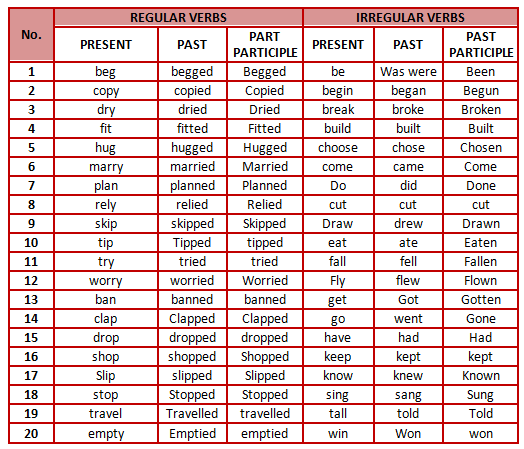
Verbs Chart
The following chart contains important verbs.
Verb Types
There are various types of verbs. Verbs show physical action, mental action, or state of being.
State of being: To be
Mental actions: To think, to guess
Physical Actions: To write, to go
Action/ Main Verbs
Definition of Action Verb
Action verb is a verb that describes an action.
Examples: Write, jump, run, eat
Zara wrote a story.
Ana eats apples.
Read another article:Parts of Speech
Action Verb List
Helping Verbs
Definition of Helping Verb
Helping verb is a word that comes before the main verb in a sentence. It helps the main verb by extending the meaning of the verb. Helping verbs have no meaning on their own.
Types of Helping Verbs
- Auxiliary Verbs
- Modal Verbs
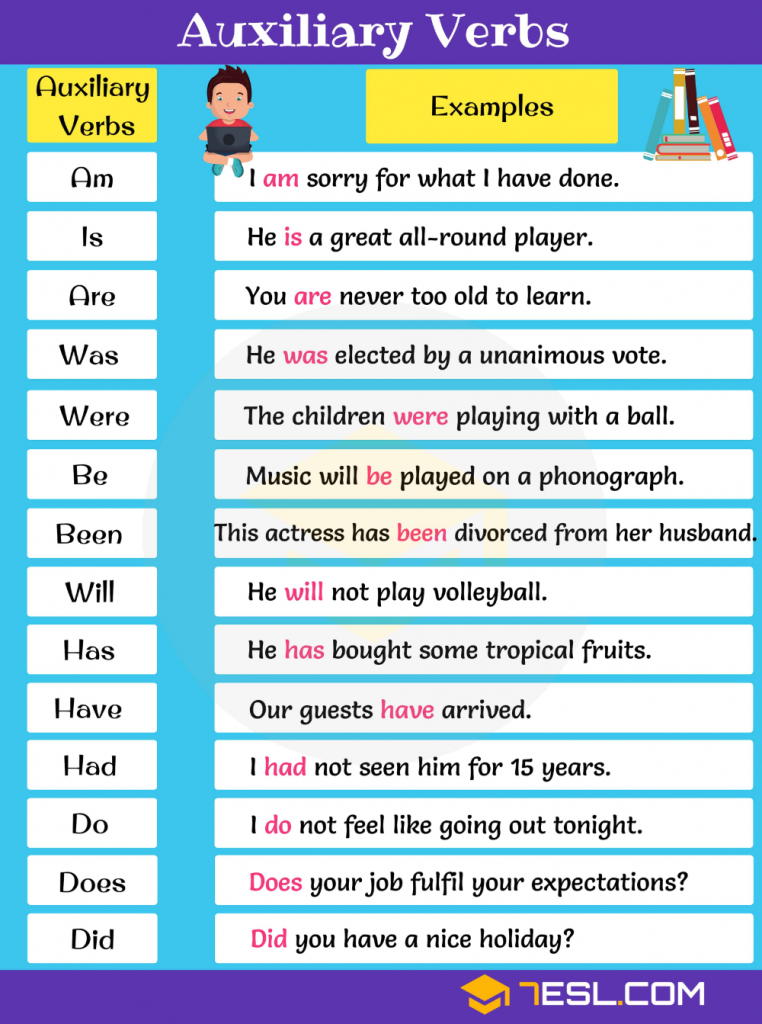
Auxiliary Verbs
Definition of Auxiliary Verb
These are the verbs that are used with another verbs to show the verb’s tense, mood or voice.
Examples: Is, am, are, was, were, be, been, being, do, does, did, have, has, had
Modal Verbs
Definition of Modal Verb
Modal verbs show obligation, possibility, impossibility, ability, inability or necessity in sentences. They are used before the main verb. They are also called as modals.
Read Another Article: Pronoun: Examples and Types
Examples: Can, could, may, might, should, must, ought to

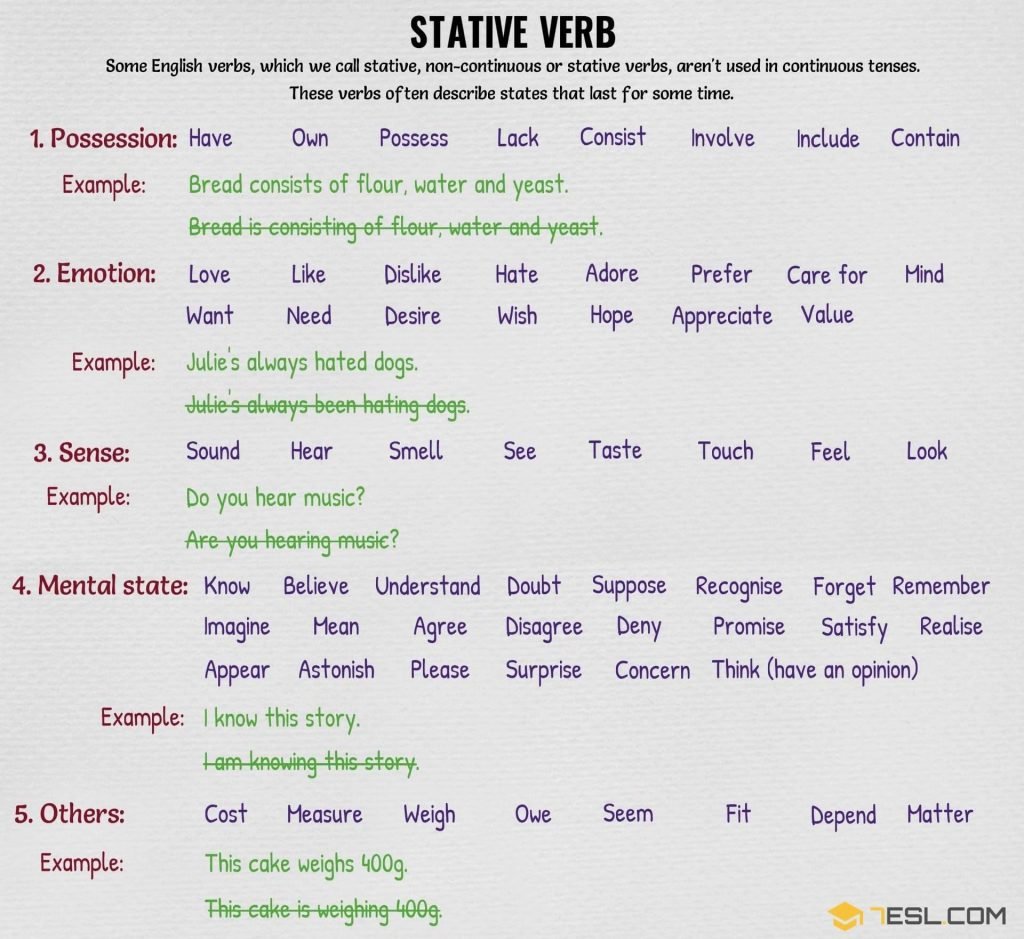
Stative Verbs
Definition of Stative Verb
Stative verbs describe a state rather than an action. They usually relate to emotions, thoughts, senses, relationships, measurements and states of being.
Examples:
Thought and opinion: Agree, believe, doubt
Feelings: Like, dislike, love
Senses: Feel, look, seem, see
Possession: Belong, have, weigh
Catenative Verbs
Definition of Catenative Verb
Catenative is a main verb that can be followed directly by another main verb. A catenative verb can link with other verbs to form a chain or series.
Examples: Ask, help, keep, promise, want, seem
They like reading stories.
Aroosh agreed to work on Sunday.
Regular Verbs
Definition of Regular Verb
Regular verbs are the verbs that can be put in the past tense simply by adding -ed or -d to the end of present tense form.
Examples:
Learn Learned
Love Loved
Irregular Verbs
Definition of Irregular Verb
Irregular verbs are the verbs that don’t add -d or -ed the end of present tense form for making past tense.
Examples:
Go went gone
Take took taken
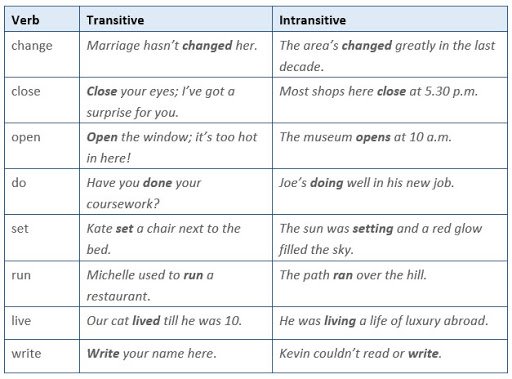
Transitive Verbs
Definition of Transitive Verb
A transitive verb is a verb that can take a direct object, which may be a noun, pronoun or noun phrase. It is an action verb showing a doable activity.
Examples:
Ana kicked the football.
She wants a smile from Adi.

Intransitive Verbs
Definition of Intransitive Verb
It is an action verb showing a doable activity and does not have a direct object.
Examples: Agree, appear, belong, fly, laugh, arrive, go, lead, occur, grow
Zubair went to the campus.
Maham arrived in the ground.
Dynamic Verbs
Definition of Dynamic Verb
A dynamic verb is a type of verb that shows the continued action on the part of the subject.
Examples:
Alia is reading a story.
I am chasing the deer.

Infinitive Verbs
An infinitive is the base form of the verb that can function as a noun, adjective, or adverb. It is preceded by ‘to‘.
Examples:
I want to run every day.
To travel was her passion.
Sumaira likes to cook.

In the end, it is very important to learn verbs as they help students and other learners to build sentences in writing. The students who use more verbs have more advanced grammatical skills. This article is highly useful for grammar learners. We have tried our best to teach the concept of verb for ease and comfort of students and learners of English grammar.
Read More:




