Adverb
Adverbs are modifiers in English grammar. They mostly modify verbs in sentences. They tell us how an action is happening.
Definition of Adverb
An adverb is a word that is used to modify a verb, adjective, clause, another adverb or even a whole sentence.
Examples of Adverbs: Always, never, often, carefully, slowly, well, now, soon, later, yet, today, yesterday, off, above, here, out, in, down, quite, too, very, almost, entirely, honestly, next, equally
Iram will be here soon.
Ahmed and Zubair often go out for dinner.
She is almost 40.
Amina dresses beautifully.
A List of Adverbs
Adverb Modifying Verb
An adverb mostly modifies verbs. It tells that how an action is happening.
Examples:
Maria was running slowly in the race.
John sings loudly in the room.
In the following sentences red colour denotes verbs and blue colour shows adverbs.

Adverb Modifying Adjective
An adverb can also modify adjectives. It can add a degree of intensity to the adjectives.
Examples:
The girl is quite beautiful.
The food was so delicious.
Your story is more interesting.

Adverb Modifying Sentence
An adverb can modify the whole sentence. Such adverbs are called sentence adverbs.
Examples:
Hopefully, we will win the match.
Honestly, most of the television comedies are vulgar.
The above each bold word modifies the whole sentence.
The following adverbs can be used as sentence adverbs.
Actually, apparently, hopefully, ideally

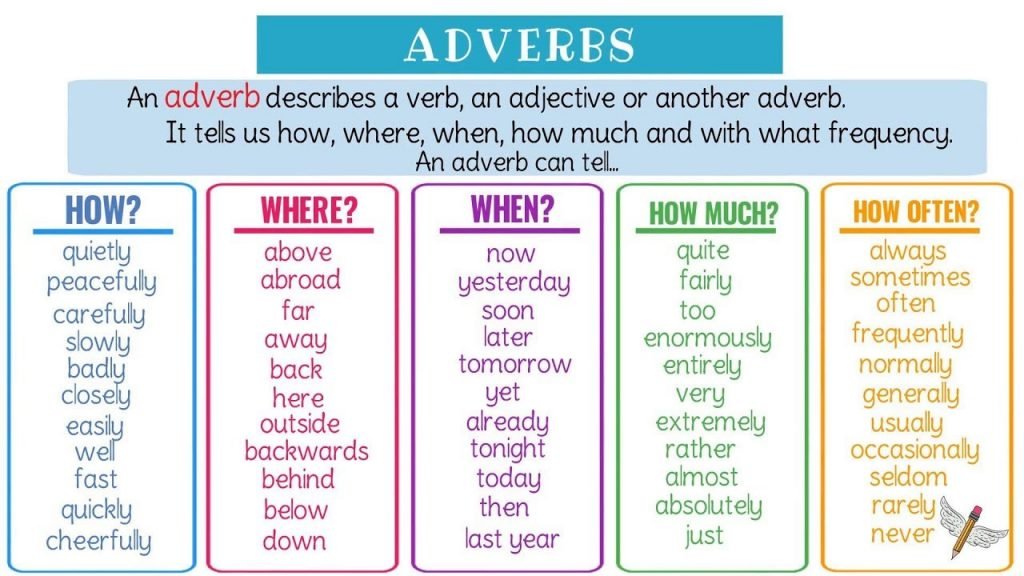
Types of Adverb
There are different types of adverbs. Each type shows different meaning. Adverbs types tell us how, where, when and with what frequency an action happens. The most important types of adverb are explained below.
- Adverbs of Time
- Adverbs of Place
- Adverbs of Manner
- Adverbs of Frequency
- Adverbs of Degree
Adverbs of Time
Adverbs of time tell us when an action happens. These adverbs are usually placed at the end of a sentence.
Examples: Now, then, today, yesterday, tomorrow, ago, soon
I will call you later.
They watched this movie last year.

Adverbs of Place
An adverb of place tells us where an action happened. Adverbs of place provide context for direction, distance and position.
Examples: Far, out, up, down, here, there, off, inside, right, towards
Mary will go there with her friend.
His child goes everywhere with him.
Humaira built a house nearby.

Adverbs of Manner
Adverbs of manner explain how an action is carried out. OR Adverbs of manner tell us how someone does something or how something happens.
These adverbs usually come after the main verb. They are mostly formed from adjectives by adding -ly to the end of adjectives.
Examples: Slowly, sweetly, warmly, calmly, kindly, sadly, well, loudly
Wania qualified the exam easily.
Horia answered the question correctly.
Sara spokes softly.
Anam drives dangerously.

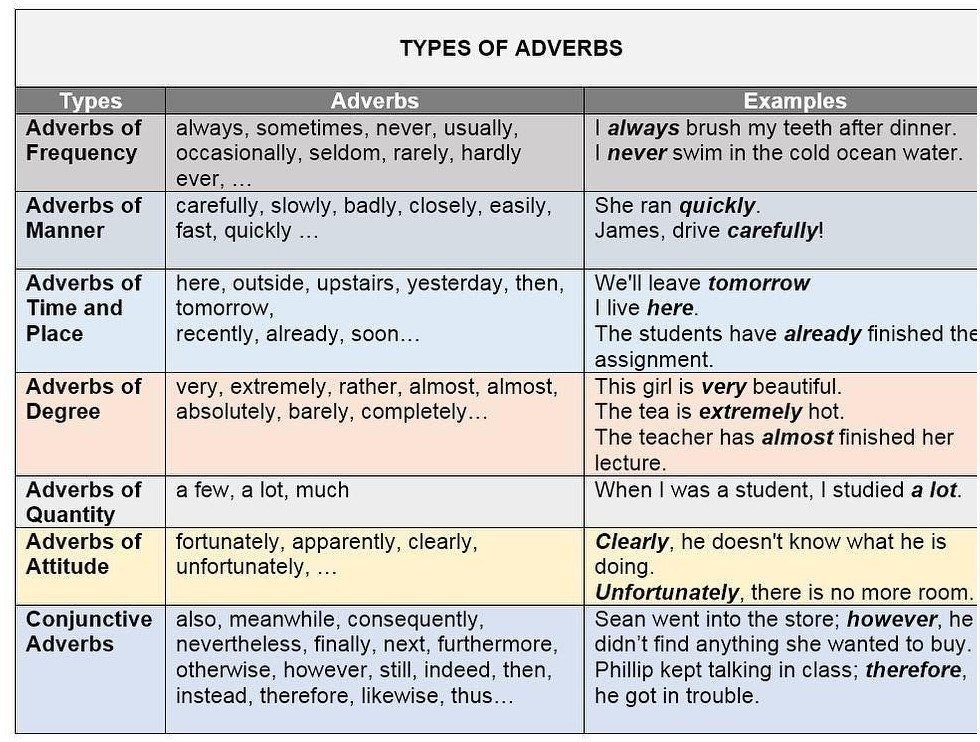
Adverbs of Frequency
Adverbs of frequency always describe how often something occurs either in definite or indefinite terms. Adverbs of frequency mostly
go before the main verb. These adverbs are used to express time or how often something occurs.
Examples: Always, usually, normally,daily, monthly, never

Adverbs of Degree
Adverbs of degree tell us the extent to which something happens. They can modify verbs, adjectives and other adverbs. They are used to show intensity or degree of something.
Examples: Very, almost, hardly, little
Yusra is extremely happy.
Thandiani is a very beautiful peak.

Adverb Types List
Position of Adverbs
Position of adverbs in the sentence depends on the type of an adverb. There are three positions for adverbs in a sentence.
Front Position
In the front position, an adverb is placed in the start of a sentence. Such adverb modifies the whole sentence.
Examples:
Fortunately, nobody was injured.
Luckily, our meal was enough for all.
Mid Position
Some adverbs come before the main verb or after the subject.
Example:
She always speak the truth.
At the End of Sentence
There are many adverbs which are placed at the end of a sentence.
Example: The child played the game quietly.

In the end, adverbs are important to learn because they perform different roles in writing. We tried our best to explain adverbs in an easy way for understanding of students and other learners of grammar.



